Description
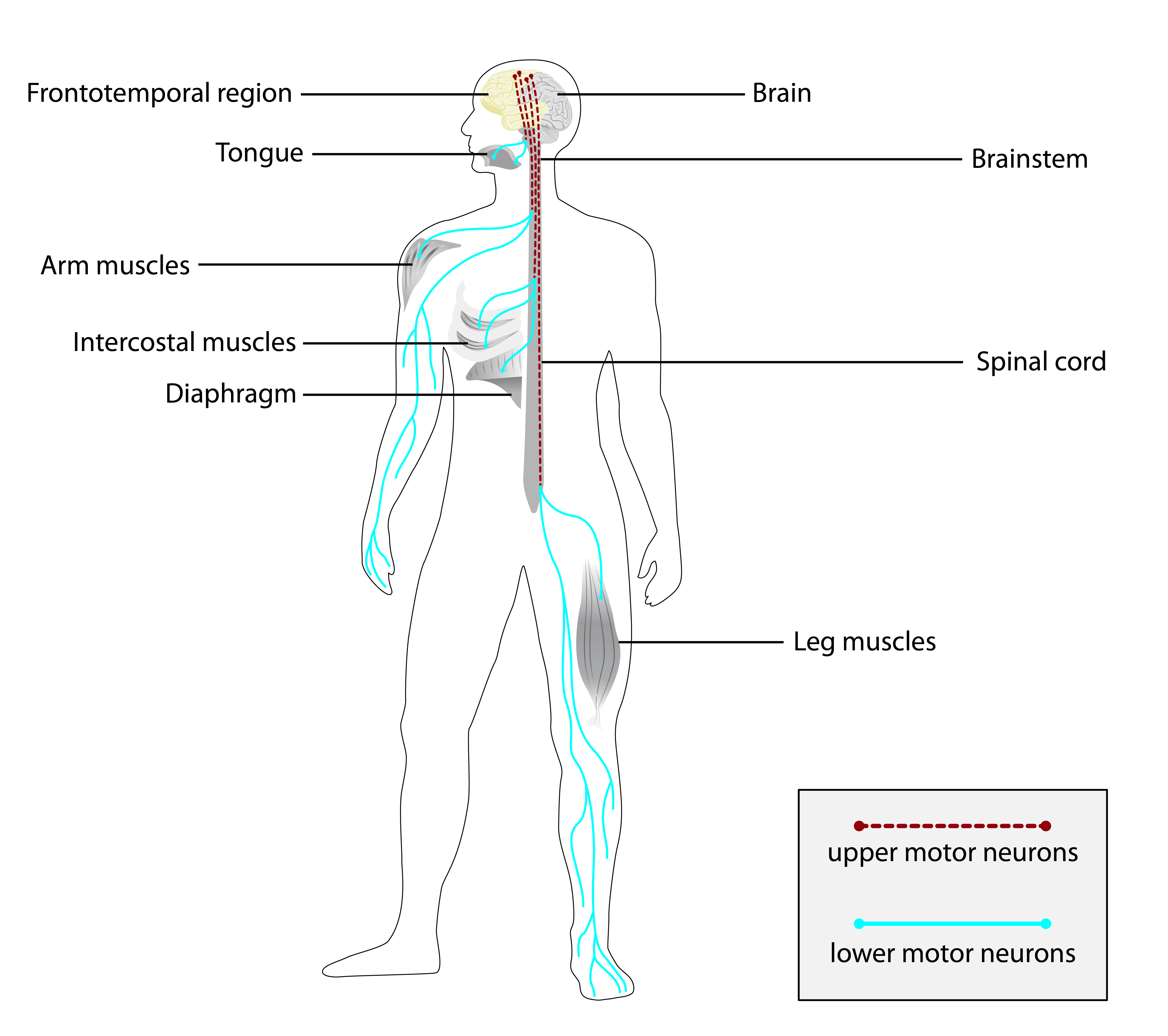
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, terminal neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and lower motor neurons that normally control voluntary muscle contraction. ALS is the most common form of the broader group of motor neuron diseases. ALS often presents in its early stages with gradual muscle stiffness, twitches, weakness, and wasting. Motor neuron loss typically continues until the abilities to eat, speak, move, and, lastly, breathe are all lost. While only 15% of people with ALS also fully develop frontotemporal dementia, an estimated 50% face at least some minor difficulties with thinking and behavior. Depending on which of the aforementioned symptoms develops first, ALS is classified as limb-onset or bulbar-onset.