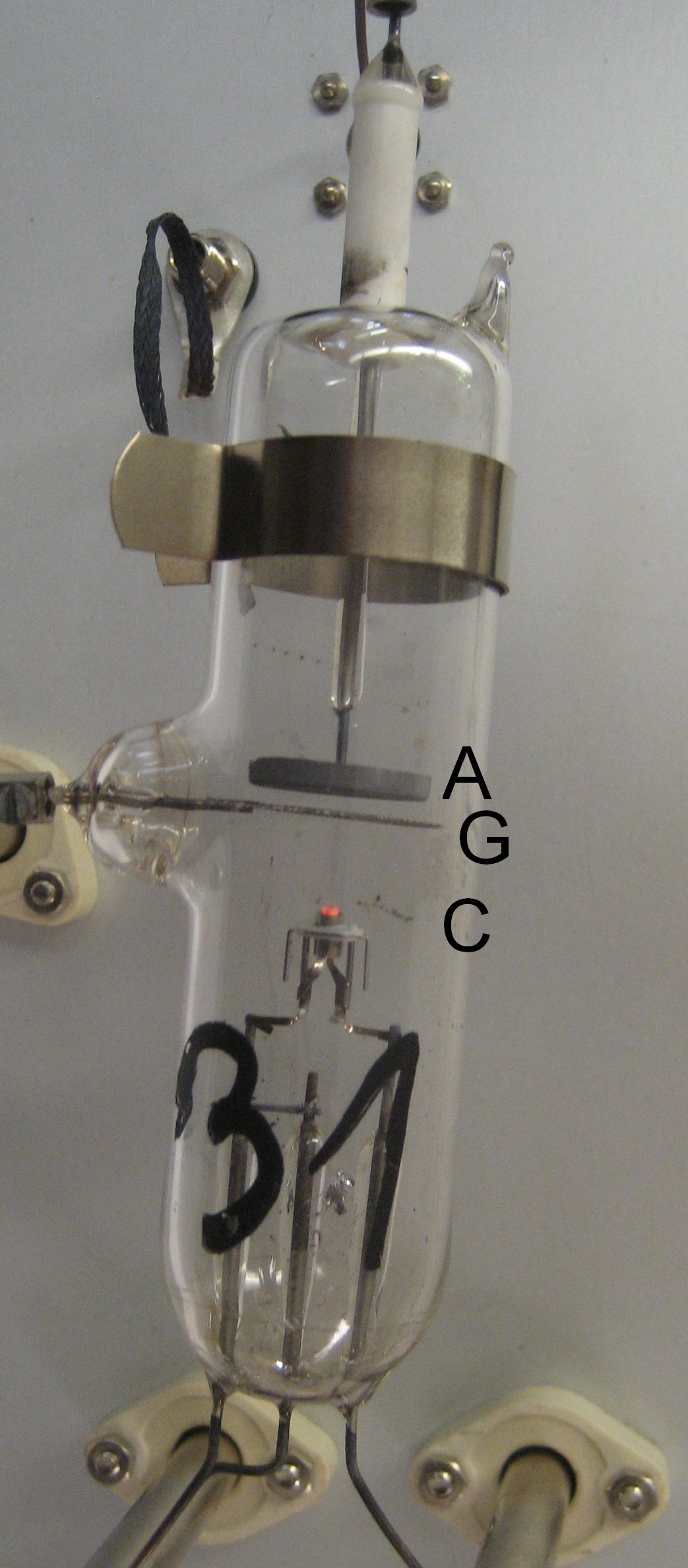
Description
The Franck–Hertz experiment was the first electrical measurement to clearly show the quantum nature of atoms. It was presented on April 24, 1914, to the German Physical Society in a paper by James Franck and Gustav Hertz. Franck and Hertz had designed a vacuum tube for studying energetic electrons that flew through a thin vapour of mercury atoms. They discovered that, when an electron collided with a mercury atom, it could lose only a specific quantity of its kinetic energy before flying away. This energy loss corresponds to decelerating the electron from a speed of about 1.3 million metres per second to zero. A faster electron does not decelerate completely after a collision, but loses precisely the same amount of its kinetic energy. Slower electrons merely bounce off mercury atoms without losing any significant speed or kinetic energy.