Description
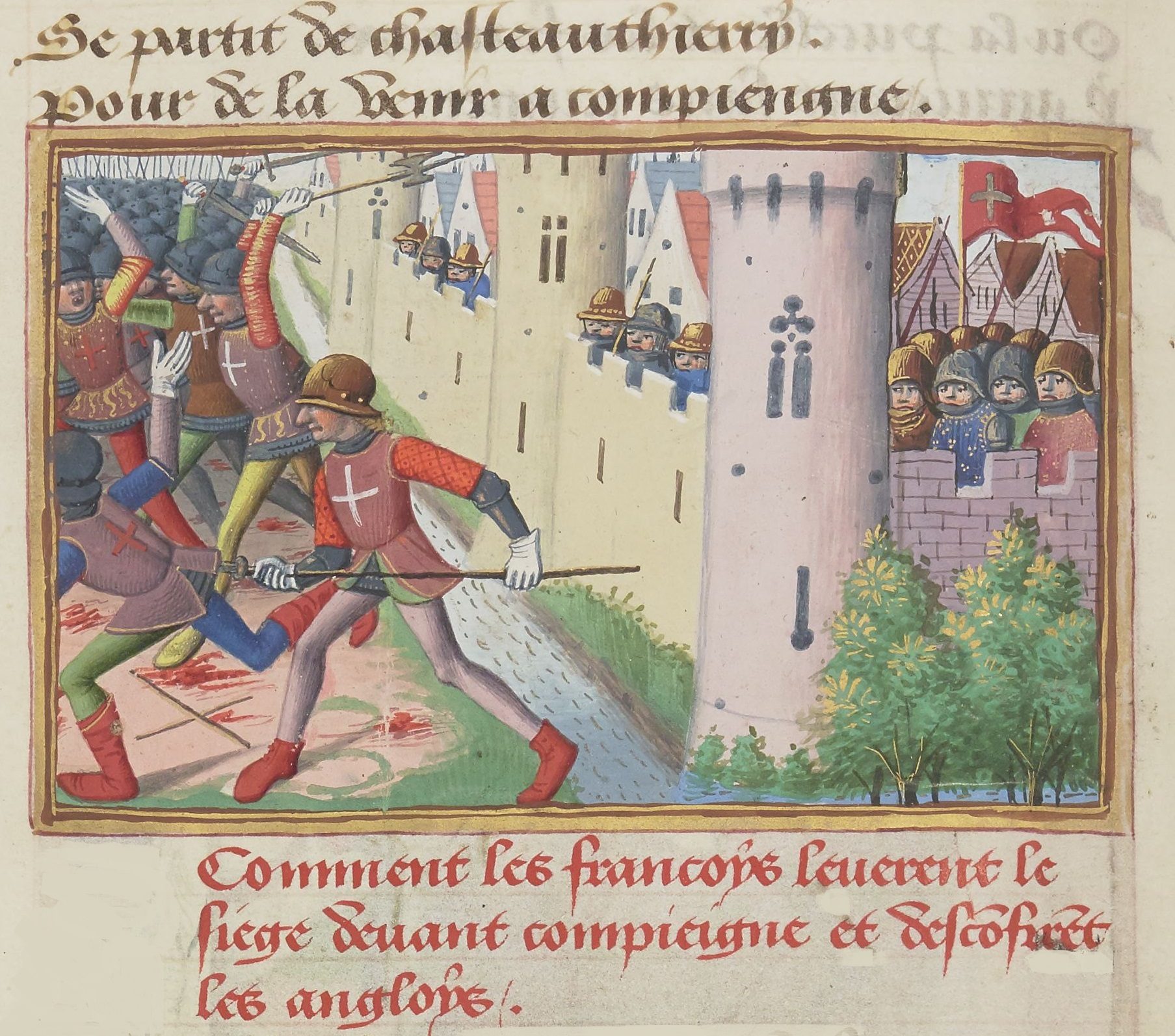
The siege of Compiègne (1430) was conducted by Duke Philip III of Burgundy after the town of Compiègne had refused to transfer allegiance to him under the terms of a treaty with Charles VII of France. The siege is perhaps best known for Joan of Arc's capture by Burgundian troops while accompanying an Armagnac force during a skirmish outside the town on 23 May 1430. Although this was otherwise a minor siege, both politically and militarily, and ultimately ended in a defeat for the Burgundians, the capture of Joan of Arc was an important event of the Hundred Years' War.